How to Draw Relational Schema From Er Diagram
To empathise this, you should have an idea nearly:
ER model
Relation model
After designing the ER diagram of organisation, nosotros need to convert information technology to Relational models which can directly be implemented by whatever RDBMS like Oracle, MySQL etc. In this commodity we will hash out how to convert ER diagram to Relational Model for unlike scenarios.
Case one: Binary Human relationship with 1:i cardinality with total participation of an entity

A person has 0 or 1 passport number and Passport is always owned by 1 person. Then it is one:1 cardinality with full participation constraint from Passport.
First Convert each entity and relationship to tables. Person table corresponds to Person Entity with key every bit Per-Id. Similarly Passport table corresponds to Passport Entity with fundamental as Pass-No. HashTable represents relationship between Person and Passport (Which person has which passport). Then it will have attribute Per-Id from Person and Pass-No from Passport.
| Person | Has | Passport | |||||
| Per-Id | Other Person Attribute | Per-Id | Pass-No | Pass-No | Other PassportAttribute | ||
| PR1 | – | PR1 | PS1 | PS1 | – | ||
| PR2 | – | PR2 | PS2 | PS2 | – | ||
| PR3 | – | ||||||
Table 1
Equally nosotros tin meet from Table i, each Per-Id and Pass-No has only i entry in Hashtabular array. And then nosotros can merge all three tables into 1 with attributes shown in Table 2. Each Per-Id volition be unique and not naught. So it will exist the key. Pass-No tin't be primal because for some person, it can exist Nil.
| Per-Id | Other Person Attribute | Pass-No | Other PassportAttribute |
Tabular array ii
Case ii: Binary Relationship with 1:1 cardinality and partial participation of both entities

A male marries 0 or ane female and vice versa as well. So it is ane:1 cardinality with partial participation constraint from both. First Convert each entity and relationship to tables. Male person tabular array corresponds to Male Entity with cardinal every bit One thousand-Id. Similarly Female table corresponds to Female Entity with cardinal as F-Id. Ally Tabular array represents human relationship betwixt Male and Female (Which Male marries which female). So it will take aspect M-Id from Male person and F-Id from Female.
| Male | Ally | Female | |||||
| M-Id | Other Male Attribute | M-Id | F-Id | F-Id | Other FemaleAttribute | ||
| M1 | – | M1 | F2 | F1 | – | ||
| M2 | – | M2 | F1 | F2 | – | ||
| M3 | – | F3 | – | ||||
Table three
As we can see from Tabular array three, some males and some females do not marry. If we merge three tables into ane, for some Yard-Id, F-Id volition exist NULL. And so there is no attribute which is ever not NULL. So we can't merge all three tables into one. We can catechumen into 2 tables. In table iv, M-Id who are married volition have F-Id associated. For others, it will exist Naught. Table 5 will accept information of all females. Primary Keys have been underlined.
| M-Id | Other Male person Attribute | F-Id |
Table 4
| F-Id | Other FemaleAttribute |
Tabular array 5
Note: Binary relationship with 1:one cardinality volition have ii table if partial participation of both entities in the relationship. If atleast 1 entity has total participation, number of tables required will be 1.
Case 3: Binary Human relationship with n: 1 cardinality

In this scenario, every student tin enroll simply in one elective course but for an constituent form there can be more than ane pupil. Starting time Convert each entity and relationship to tables. Student table corresponds to Pupil Entity with key as S-Id. Similarly Elective_Course tabular array corresponds to Elective_Course Entity with key every bit East-Id. Enrolls Table represents relationship between Student and Elective_Course (Which student enrolls in which course). So it will take attribute S-Id from and Student Due east-Id from Elective_Course.
| Student | Enrolls | Elective_Course | |||||
| Southward-Id | Other Educatee Aspect | Due south-Id | E-Id | East-Id | Other Constituent CourseAttribute | ||
| S1 | – | S1 | E1 | E1 | – | ||
| S2 | – | S2 | E2 | E2 | – | ||
| S3 | – | S3 | E1 | E3 | – | ||
| S4 | – | S4 | E1 | ||||
Table vi
As we can see from Table half dozen, S-Id is not repeating in Enrolls Tabular array. So it can be considered as a key of Enrolls tabular array. Both Student and Enrolls Tabular array's central is same; we can merge information technology as a unmarried tabular array. The resultant tables are shown in Table 7 and Table 8. Master Keys have been underlined.
| Southward-Id | Other Student Attribute | Due east-Id |
Table 7
| East-Id | Other Constituent CourseAttribute |
Table 8
Case iv: Binary Relationship with m: northward cardinality
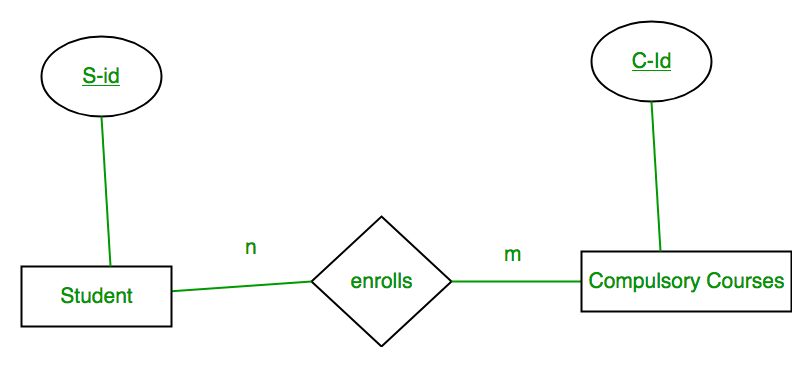
In this scenario, every student tin can enroll in more than 1 compulsory course and for a compulsory course there can be more than ane educatee. Showtime Convert each entity and human relationship to tables. Educatee table corresponds to Educatee Entity with key equally S-Id. Similarly Compulsory_Courses table corresponds to Compulsory Courses Entity with key as C-Id. Enrolls Table represents human relationship betwixt Pupil and Compulsory_Courses (Which student enrolls in which form). So it will take attribute S-Id from Person and C-Id from Compulsory_Courses.
| Pupil | Enrolls | Compulsory_Courses | |||||
| Due south-Id | Other Student Aspect | S-Id | C-Id | C-Id | Other Compulsory CourseAttribute | ||
| S1 | – | S1 | C1 | C1 | – | ||
| S2 | – | S1 | C2 | C2 | – | ||
| S3 | – | S3 | C1 | C3 | – | ||
| S4 | – | S4 | C3 | C4 | – | ||
| S4 | C2 | ||||||
| S3 | C3 | ||||||
Table ix
As we can run into from Tabular array 9, S-Id and C-Id both are repeating in Enrolls Table. But its combination is unique; so it can be considered as a key of Enrolls table. All tables' keys are different, these can't exist merged. Master Keys of all tables have been underlined.
Case 5: Binary Human relationship with weak entity

In this scenario, an employee can take many dependents and ane dependent tin depend on one employee. A dependent does non accept whatsoever existence without an employee (due east.g; you as a child can be dependent of your male parent in his company). So it will exist a weak entity and its participation will always be full. Weak Entity does not have central of its ain. So its primal will exist combination of key of its identifying entity (Eastward-Id of Employee in this case) and its fractional key (D-Proper name).
First Convert each entity and human relationship to tables. Employee table corresponds to Employee Entity with cardinal as E-Id. Similarly Dependents table corresponds to Dependent Entity with central equally D-Name and E-Id. HashTable represents human relationship betwixt Employee and Dependents (Which employee has which dependents). So it will take attribute E-Id from Employee and D-Proper name from Dependents.
| Employee | Has | Dependents | ||||||
| Eastward-Id | Other Employee Attribute | Due east-Id | D-Proper name | D-Proper noun | E-Id | Other DependentsAttribute | ||
| E1 | – | E1 | RAM | RAM | E1 | – | ||
| E2 | – | E1 | SRINI | SRINI | E1 | – | ||
| E3 | – | E2 | RAM | RAM | E2 | – | ||
| E3 | ASHISH | ASHISH | E3 | – | ||||
Table 10
Equally we can see from Tabular array x, E-Id, D-Name is fundamental for Has as well as Dependents Table. Then we tin merge these two into 1. So the resultant tables are shown in Tables 11 and 12. Primary Keys of all tables have been underlined.
| East-Id | Other Employee Attribute |
Table 11
| D-Name | E-Id | Other DependentsAttribute |
Tabular array 12
Article contributed past Sonal Tuteja. Delight write comments if y'all find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed higher up
How to Draw Relational Schema From Er Diagram
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/mapping-from-er-model-to-relational-model/
Post a Comment for "How to Draw Relational Schema From Er Diagram"